This page is part of the E3G Public Bank Climate Tracker Matrix, our tool to help you assess the Paris alignment of public banks, MDBs and DFIs
| Paris Alignment | Reasoning |
| Paris aligned | Dedicated strategy for climate risk at project level. Climate strategy takes beyond-project approach to client resilience |
| Project-level climate risk management procedures | Scope of coverage of project-level climate risk management | Enhancing client climate resilience | Adaptation finance |
| ADB has a specific strategy for “Climate Risk Management in ADB Projects”, involving both risk screening and risk-proofing | ADB screens all projects for climate risks; a subset of these are examined for climate-proofing options | There are clear efforts made to move clients towards climate resilience and beyond climate proofing | ADB has slowly increased its levels of adaptation finance although it is still relatively low |
Explanation
All ADB projects are screened for climate risks. Initial screenings are made, and projects deemed to be medium or high risk undergo detailed climate risk and adaptation assessment, using dedicated tools such as AWARE for Projects. Once completed, a technical and economic evaluation of the adaptation options is undertaken, followed by identification of the most appropriate climate-proofing options. Lastly, the ADB monitoring and reporting system records the risk assessment and adaptation measures.
Addressing climate change (including building climate and disaster resilience) is one of ADB’s seven operational priorities for its Strategy 2030. ADB’s Climate Change Operational Framework aims to support national policy reform, mainstreaming of climate actions into development planning, building institutional capacities, promoting policy coordination and harmonisation, and efforts to translate NDCs into investment plans—as well as enhancing climate resilience beyond climate-proofing.
ADB has slowly increased its level of adaptation finance although this is still low, both in absolute terms and in relative terms compared with peer adaptation-to-mitigation finance ratios (see Figure below).
Figure : Climate-related finance reported to the OECD-DAC over 2012 to 2017 (USD billion)
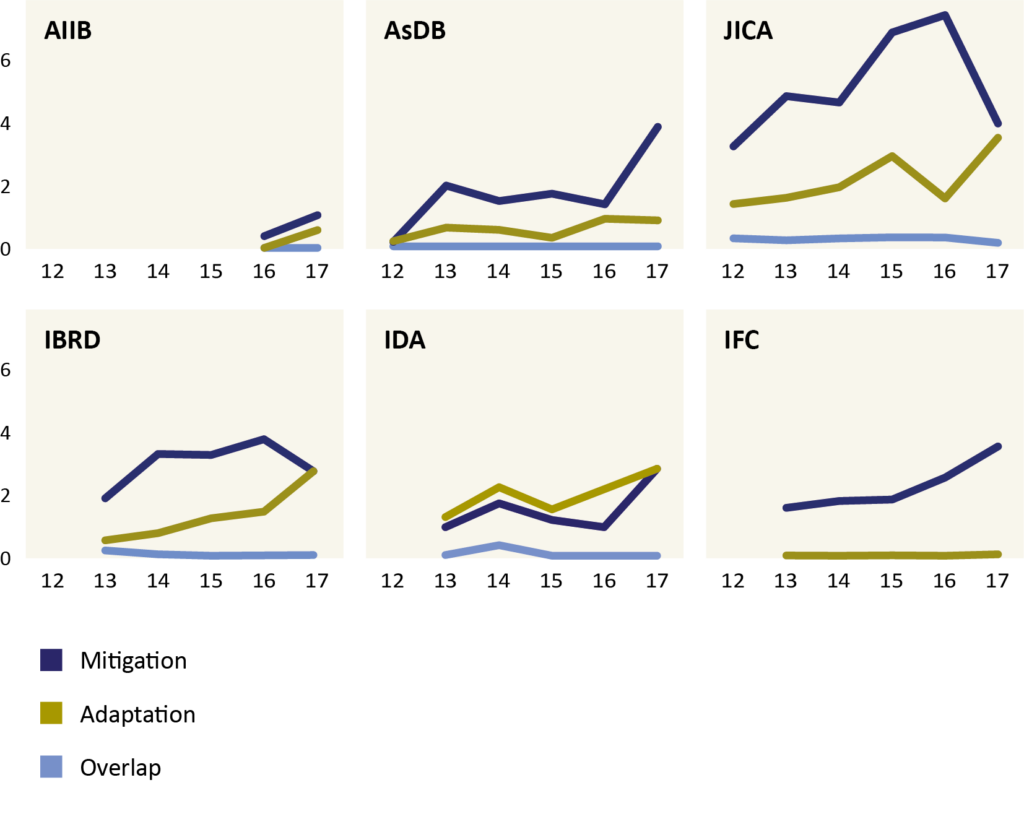
Source: E3G analysis of climate-related development finance from OECD-DAC.*
*Overlap finance refers to projects which contribute towards both adaptation and mitigation activities.